What Are IoT Management Platforms?
IoT management platforms are comprehensive systems that enable the monitoring, management, and control of a diverse range of connected devices within an IoT ecosystem. They provide tools for device provisioning, configuration, firmware updates, and troubleshooting, ensuring devices operate efficiently and securely.
These platforms also enable data collection, analysis, and visualization, helping organizations optimize performance and make informed decisions. Modern IoT deployments can include thousands to millions of heterogeneous devices, each with its own requirements for connectivity, updates, and security. IoT management platforms help manage this complexity by offering device provisioning, remote monitoring, automation, and analytics in one place.
Key functions of IoT management platforms include:
- Device provisioning and onboarding: Platforms simplify the process of adding new devices to the network, simplifying initial setup and configuration.
- Remote configuration and control: Administrators can remotely configure device settings, update firmware, and manage device behavior, even from a distance.
- Real-time monitoring and alerting: Platforms provide real-time visibility into device status, performance, and potential issues, enabling timely responses to anomalies.
- Data management and analytics: They collect and store data from connected devices, offering tools for analysis, visualization, and reporting to gain insights and optimize operations.
- Security and access control: Robust security features ensure that devices and data are protected from unauthorized access and cyber threats.
- Connectivity management: Platforms manage communication protocols and network connections for devices, ensuring reliable and efficient data exchange.
- Lifecycle management: They support the entire device lifecycle, from initial setup to decommissioning, including maintenance, updates, and eventual replacement.
Choosing the right IoT management platform depends on the specific needs of the organization, including the type and number of devices, desired functionalities, and budget considerations. Organizations should carefully evaluate their requirements and compare different platforms to find the best fit.
This is part of a series of articles IoT networking
Key Functions of IoT Management Platforms
Connectivity Management
Connectivity management enables secure, efficient data transmission between IoT devices and backend services. IoT environments can include a range of connection types cellular, Wi-Fi, Ethernet, LPWAN, or satellite—each with its own performance characteristics and operational requirements. A management platform centralizes the monitoring and orchestration of these connections, providing real-time visibility and control over network status and performance.
With thousands of devices requiring constant and reliable communication, organizations must manage factors like bandwidth allocation, roaming, and network failovers. Advanced platforms allow administrators to monitor connectivity health, detect and resolve outages, and optimize traffic to avoid unnecessary costs. Tools for remote SIM management, device grouping, and automated network selection reduce manual intervention.
Learn more in our detailed guide to IoT connectivity platforms
Device Provisioning and Onboarding
Device provisioning involves assigning unique identities and credentials to new devices, configuring their primary settings, and ensuring their secure connection to the network. An efficient onboarding process helps automate initial configuration and enrollment, reducing manual errors and minimizing the time required to bring new devices online.
A seamless onboarding process is important for large-scale deployments, allowing organizations to add devices in batches and manage them according to pre-established templates or rules. This also ensures devices immediately comply with organizational standards for security and communication. Modern platforms often provide self-service and zero-touch provisioning features, where devices automatically connect and configure themselves.
Remote Configuration and Control
Remote configuration and control capabilities allow administrators to update device settings, deploy firmware upgrades, and change operational parameters without onsite intervention. This is essential for distributed IoT environments, where manual device management would be impractical due to scale or geographic dispersion. Platforms offer dashboards and APIs to push configuration changes across fleets of devices simultaneously.
Continuous device optimization ensures performance, energy efficiency, and security. By centrally controlling parameters like power usage profiles, sensor calibration, or application-specific settings, organizations maintain optimal device behavior and compliance without dispatching service personnel. Scheduled updates, role-based access controls, and audit trails further help minimize downtime and track configuration changes.
Real-Time Monitoring and Alerting
Real-time monitoring provides continuous visibility into the status, health, and behavior of IoT devices and their connections. Through dashboards and reporting tools, administrators can track metrics such as device uptime, battery status, data throughput, and error rates. Prompt detection of anomalies or deteriorating conditions is vital for maintaining device fleets and preempting potential issues.
Alerting mechanisms supplement monitoring by notifying personnel when critical thresholds—like network failures, sensor anomalies, or unexpected device behavior—are breached. Automated notifications by email, SMS, or messaging apps enable rapid response and issue resolution.
Data Management and Analytics
Data management and analytics are central to extracting value from IoT deployments. Platforms collect vast amounts of sensor and event data and provide tools for storage, normalization, enrichment, and integration with enterprise systems. Simplified data flows enable organizations to correlate device information with external sources, fuel process automation, and trigger meaningful actions.
Analytics capabilities extend beyond reporting; they include machine learning model deployment, anomaly detection, trend analysis, and automated notifications based on data patterns. With these tools, organizations can optimize operations, predict maintenance needs, and uncover new insights.
Security and Access Control
Security and access control protect IoT deployments by managing user and device authentication, data encryption, and policy enforcement. IoT platforms enforce security best practices such as multi-factor authentication, secure credential storage, and encrypted data transmission, protecting against unauthorized access and data breaches.
Role-based access controls (RBAC) restrict functionality and sensitive data views to authorized users, reducing internal risk and ensuring operational compliance. Audit logging tracks actions for accountability and compliance checks. Comprehensive security frameworks—integrated with monitoring and alerting services—enable organizations to react swiftly to threats and maintain a strong defense posture amidst evolving risks in the IoT landscape.
Lifecycle Management
Lifecycle management in IoT refers to overseeing a device’s journey from initial provisioning to eventual decommissioning. Throughout this process, administrators must manage firmware updates, policy enforcement, hardware replacements, and the gradual retirement of obsolete devices. Platforms automate these tasks to help minimize manual effort and ensure devices remain compliant with operational standards throughout their lifecycle.
End-of-life management is just as critical as onboarding. Decommissioning involves securely removing a device’s authentication, wiping sensitive data, and recording its retirement for audit purposes. Effective lifecycle management helps reduce operational risk, control costs by preventing device sprawl, and maintain the security and reliability of the IoT ecosystem.
Related content: Read our guide to IoT connectivity platforms
Notable IoT Management Platforms
1. floLIVE

loLIVE is a leading IoT management platform built specifically for global IoT connectivity and device lifecycle management. Unlike traditional platforms, it provides a cloud-native (Utilising a multi-cloud strategy), globally distributed core network optimized for IoT.
Key features include:
- Global Multi-IMSI SIMs & eSIM support – Seamless cross-border device deployments with dynamic network switching.
- Regulatory compliance by design – Local core networks ensure data sovereignty across regions.
- Centralized SIM & device management – A single portal to provision, monitor, and control millions of devices at scale.
- IoT-optimized billing & usage monitoring – Flexible pricing models for low-bandwidth, high-volume IoT applications.
- Security-first architecture – Private APNs, VPN integration, and traffic segregation for enterprise-grade security.
With floLIVE, organizations can launch IoT services faster, scale globally, and remain compliant locally, all while reducing operational costs and complexity.mandates.

2. AWS IoT Core

AWS IoT Core is a managed cloud service that enables secure, scalable communication between connected devices and the AWS cloud. It serves as the central hub for integrating IoT hardware with AWS services, supporting real-time messaging, device provisioning, and data routing.
Key features include:
- Multi-protocol support: Supports MQTT, MQTT over WebSockets, HTTPS, and LoRaWAN.
- Message broker: Routes messages between devices and applications using publish/subscribe and request/response patterns.
- LoRaWAN integration: Manages LoRaWAN devices without requiring a separate LoRaWAN Network Server.
- Device SDKs and APIs: Offers SDKs and APIs for building device applications and managing IoT workflows.
- Management interfaces: Includes AWS CLI, REST APIs, and a web console for managing devices, certificates, jobs, and policies.
3. Microsoft Azure IoT Hub
Azure IoT Hub is a managed cloud service that enables secure, bi-directional communication between IoT devices and cloud-based applications. Acting as the central message broker in an IoT architecture, it supports large-scale deployments involving millions of devices and enables real-time telemetry, command execution, and device configuration.
Key features include:
- Scalable message routing: Routes messages to various Azure services such as storage, event hubs, and service bus based on message content and routing rules.
- Bi-directional messaging: Supports device-to-cloud telemetry, cloud-to-device commands, file uploads, and direct method invocation using a request-reply model.
- Device identity and authentication: Uses an identity registry for device management and supports both SAS token and X.509 certificate-based authentication.
- Secure communication: Secures all device interactions using transport layer security (TLS), with support for TLS 1.2 as the recommended option.
- Device twins and plug and play: Enables synchronization of device state and metadata between the device and cloud through readable and writable properties.
4. Cisco IoT Cloud Connect

Cisco IoT Control Center – Cloud Connect is a cloud-powered platform to simplify and secure large-scale IoT device connectivity, data aggregation, and lifecycle management. As an optional feature of Cisco IoT Control Center, Cloud Connect addresses key challenges in IoT environments, such as limited device storage, security enforcement, and complex onboarding.
Key features include:
- Device-to-cloud integration: Simplifies secure connectivity between IoT devices and cloud-based hubs using automated provisioning and TLS encryption.
- Centralized data aggregation: Consolidates telemetry streams from distributed sensors and devices into a secure cloud environment for unified storage, analysis, and management.
- Optimized storage utilization: Offloads data from resource-constrained devices using techniques like compression, aggregation, and prioritization to preserve local resources.
- Security framework: Enforces authentication via IoT SAFE SIM applets, supports encrypted communication, and centrally manages certificates and policies.
- Zero-touch provisioning: Automates onboarding by assigning credentials and enabling devices to connect securely without manual configuration.
Source: Cisco
5. Radix IoT
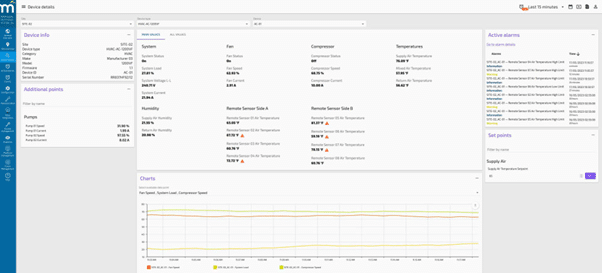
Radix IoT is a centralized, cloud-native platform to unify and manage operational data from distributed infrastructure at scale. Built around its core product, Mango, the solution helps organizations gain visibility and control across a range of assets from data centers and telecom sites to energy grids and smart buildings.
Key features include:
- Mango IoT platform: A flexible, web-based platform that runs on edge hardware or in the cloud, enabling centralized management of distributed systems.
- System and device unification: Integrates data from diverse equipment, software, and protocols across multiple sites into a single interface.
- Monitoring and management: Supports live status updates, remote triage, and operational control, reducing the need for onsite intervention.
- Historical and live data insights: Combines real-time telemetry with historical trends to drive immediate actions and long-term planning.
- Scalable architecture: Designed to scale from a few devices to thousands of locations and millions of data points, with no drop in performance.
Cumulocity IoT
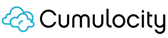
Cumulocity IoT is an AI-powered platform that enables organizations to securely connect, manage, and analyze data from industrial devices. Designed to bridge the gap between device connectivity and data-driven innovation, it simplifies the deployment of IoT solutions across industries such as manufacturing, healthcare, utilities, logistics, and retail.
Key features include:
- Device onboarding: Connect industrial devices and start managing them within minutes using pre-integrated templates for 170+ device types.
- Lifecycle device management: Manage connected assets through their full lifecycle—from registration to updates and decommissioning—through an intuitive UI.
- Remote monitoring and diagnostics: Monitor equipment in real time to reduce downtime, increase reliability, and improve customer satisfaction.
- AI-powered insights: Analyze telemetry for anomaly detection, performance optimization, and predictive maintenance using built-in AI and analytics capabilities.
- Edge-to-cloud flexibility: Run applications at the edge or in the cloud, supporting resource-constrained environments and global deployments.
Source: Cumulocity
7. OpenRemote

OpenRemote is an open-source IoT platform for manufacturers and system integrators to build and manage large-scale IoT solutions. With a flexible architecture and strong community support, it enables secure device onboarding, real-time monitoring, rules-based automation, and user-specific application development.
Key features include:
- Secure device onboarding: Supports auto-provisioning via MQTT, HTTP, or WebSocket APIs, creating digital twins and enabling live status tracking and firmware management.
- Rules engine and alerts: Automate behavior with a visual drag-and-drop rules editor or advanced scripting, triggering actions and notifications based on real-time data.
- Data visualization: Collect, process, and display data through customizable dashboards built with a flexible widget library to deliver insights to both internal teams and end users.
- Multi-tenant architecture: Provide isolated environments for distributors or service partners, enabling them to manage devices and define their own automation without central support.
- Custom applications: Use modular web components to build branded apps for installers and customers.

Source: OpenRemote
8. ThingsBoard

ThingsBoard is an open-source IoT platform that provides device management, data collection, real-time processing, and visualization. Designed to support both cloud and on-premises deployments, it enables organizations to build scalable, fault-tolerant IoT applications using standard protocols like MQTT, CoAP, and HTTP.
Key features include:
- Multi-protocol device connectivity: Supports MQTT, CoAP, and HTTP for connecting a wide range of IoT devices across industrial and commercial use cases.
- Entity and asset management: Provision, organize, and manage devices, assets, and their relationships using secure, server-side APIs with support for customer-specific hierarchies.
- Scalable telemetry collection: Ingest and store large volumes of time-series telemetry data with built-in redundancy and fault tolerance to ensure data integrity at scale.
- Custom dashboards and widgets: Visualize real-time and historical data using configurable dashboards and widget libraries; share visualizations with internal teams or customers.
- Rule engine for event processing: Define rule chains to process incoming telemetry, generate alarms, normalize data, or trigger automated actions based on events or device state.
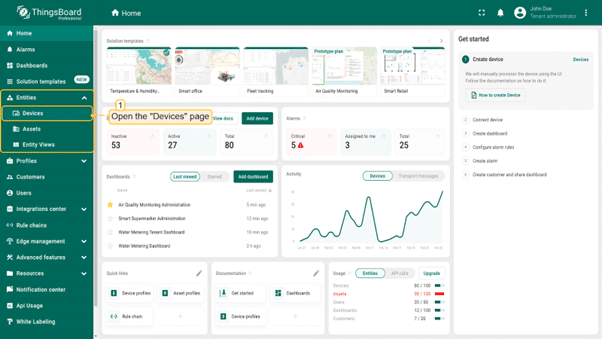
Source: ThingsBoard
Comparison Table
| Platform | Type | Strengths | Best For |
| floLIVE | Cloud-native IoT connectivity & device management | Global multi-IMSI/eSIM support, regulatory compliance, centralized SIM/device lifecycle management, security-first design | Enterprises & MVNOs needing global IoT connectivity, compliance, and scalability |
| AWS IoT Core | Cloud platform (AWS ecosystem) | Strong integration with AWS services, multi-protocol support, scalable data routing | Enterprises already invested in AWS cloud |
| Azure IoT Hub | Cloud platform (Microsoft ecosystem) | Bi-directional messaging, device twins, enterprise system integration | Enterprises using Microsoft Azure stack |
| Cisco IoT Control Center | Connectivity management (SIM-focused) | Carrier-grade connectivity, security, zero-touch provisioning | MNOs/MVNOs, enterprises with cellular IoT focus |
| Cumulocity IoT | Industrial IoT platform | Device onboarding, AI-powered insights, edge-to-cloud deployments | Manufacturing, healthcare, utilities needing industrial IoT analytics |
| Radix IoT (Mango) | Operational infrastructure management | Unifies data from telecom, energy, and smart buildings; scalable monitoring | Large distributed sites needing infrastructure visibility |
| OpenRemote | Open-source IoT platform | Customizable, rules-based automation, multi-tenant | Manufacturers & integrators seeking open-source flexibility |
| ThingsBoard | Open-source IoT platform | Multi-protocol connectivity, custom dashboards, event rule engine | Developers & enterprises needing flexible, scalable, low-cost IoT platform |
Choosing the Right IoT Management Platform
Selecting an IoT management platform requires careful evaluation of technical and operational requirements. The right choice depends on the scale, industry, and specific use cases of the IoT deployment::
- Device and protocol compatibility: Ensure the platform supports the types of devices you plan to use and communication protocols such as MQTT, CoAP, HTTP, or LoRaWAN. Compatibility affects integration speed and system stability.
- Scalability and performance: Look for platforms that can handle your current device volume and scale seamlessly as your fleet grows. Performance under load, especially during high-throughput operations, is critical.
- Deployment flexibility (cloud vs. edge vs. hybrid): Depending on latency requirements and network constraints, choose a platform that supports cloud, edge, or hybrid deployments. Edge capabilities are vital for real-time control in remote locations.
- Security and compliance: Assess the platform’s ability to enforce secure device communication, access control, data encryption, and audit logging. Support for industry-specific compliance standards is essential in regulated sectors.
- Data handling and integration: Evaluate data storage, normalization, and analytics capabilities. Integration with enterprise systems (e.g., ERP, CRM, analytics platforms) and APIs for custom development is also important.
- Operational tools and automation: Features like zero-touch provisioning, firmware updates, rule engines, and remote troubleshooting tools reduce manual overhead and improve reliability.
- Ecosystem and vendor support: A mature ecosystem with good documentation, SDKs, support options, and community activity can significantly reduce time-to-market and long-term maintenance effort.
- Cost and licensing model: Compare pricing models—subscription-based, usage-based, or open-source—and understand hidden costs related to scaling, premium features, or third-party integrations.
Learn more in our detailed guide on IoT platforms for enterprises
Conclusion
IoT management platforms play a vital role in ensuring connected devices are deployed, maintained, and scaled efficiently across diverse environments. By centralizing control, enhancing security, and enabling automation, these platforms help organizations reduce operational complexity and unlock the full value of their IoT investments.





